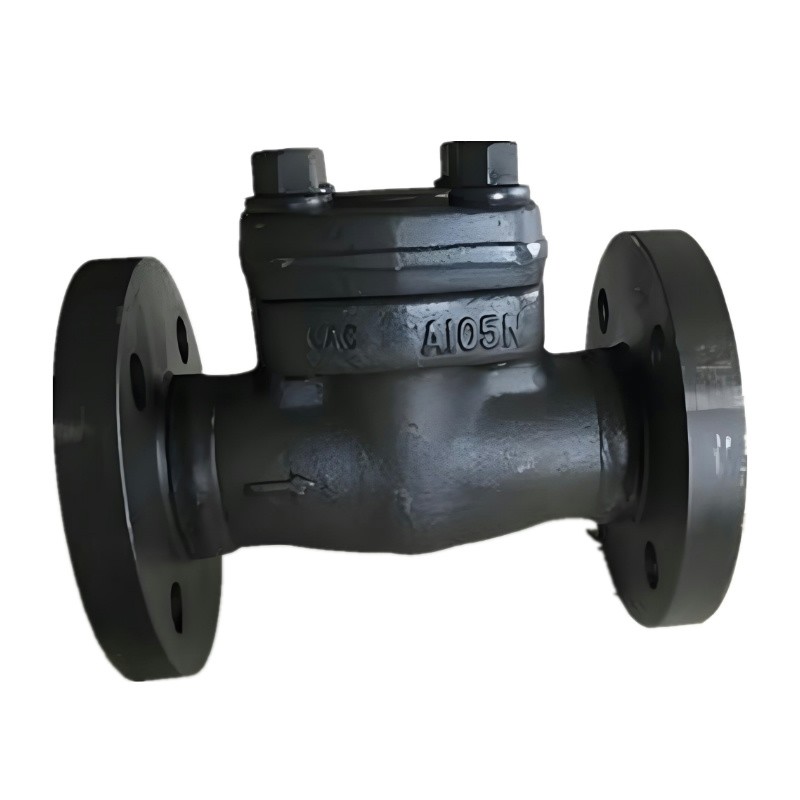
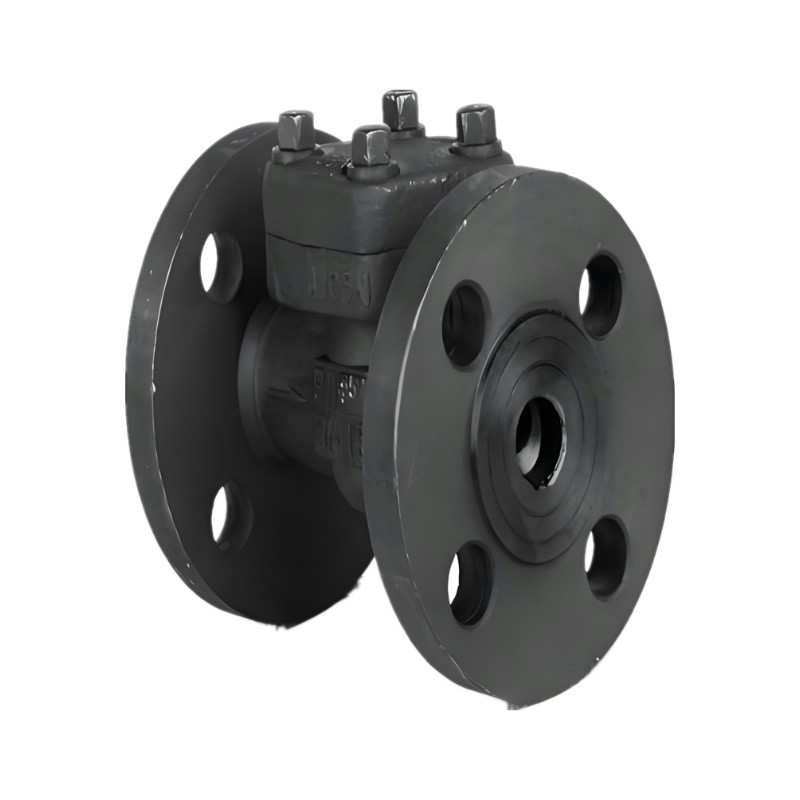
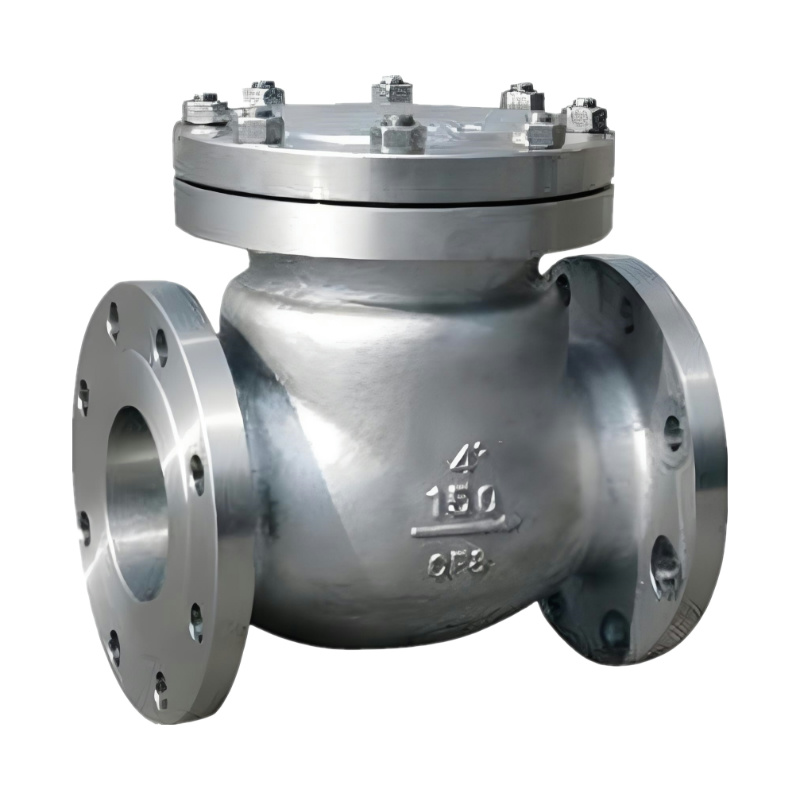
Forged Steel Lift Check Valve
Introduction
This article contains all the information you need to know about Forged Steel Lift Check Valve
Read further and learn more about:
Specification
Types
Application
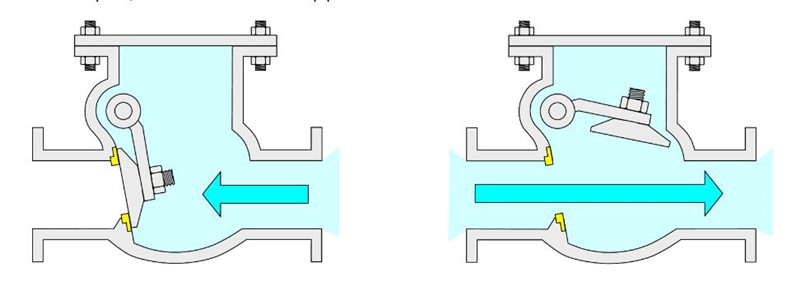
Chapter 1 - Specification
Here's a typical specification for a forged steel lift check valve:
Body Material
Forged steel, typically ASTM A105 (carbon steel), ASTM A182 F316 (stainless steel), ASTM A182 F22 (chromium molybdenum steel), or other suitable materials for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Trim Material:
The trim materials are typically selected based on the fluid characteristics and service conditions. Common trim materials include stainless steel (ASTM A276 Type 316, ASTM A276 Type 304), carbon steel (ASTM A105), or other suitable alloys for erosion and corrosion resistance.
Seat Material:
Seats are usually made of materials such as stainless steel, stellite, or other hardened materials for excellent wear resistance and sealing performance.
Valve Size
Available in various sizes typically ranging from 1/2" to 2" (larger sizes may be available upon request).
Bonnet Type:
Bolted bonnet design, allowing for easy maintenance and repair. Pressure seal bonnet design may also be available for high-pressure applications.
Pressure Rating
ANSI Class 800, 1500, or 2500, indicating the maximum pressure the valve can withstand. The selection of pressure rating depends on the specific application requirements.
Temperature Range
Suitable for operating temperatures ranging from -29°C to 593°C (-20°F to 1100°F) or higher, depending on material selection and pressure rating.
End Connections
Socket weld or threaded ends conforming to ASME B16.11 standards. Flanged ends may also be available upon request.
Design Standards:
The valve design should comply with international standards such as API 602, ASME B16.34, or equivalent for construction, design, and testing requirements.
Compliance:
The valve should comply with relevant industry standards and regulations such as ASME, ANSI, API, ASTM, MSS-SP, and others, depending on the application and location.
Chapter 2 - Forged Steel Lift Check Valve Types
Forged steel lift check valves are available in several types, each designed to meet specific application requirements and operating conditions. Here are some common types of forged steel lift check valves:

Bolted Bonnet Lift Check Valve:
This is the most common type of forged steel lift check valve. It features a bolted bonnet design, allowing for easy access to the internals for maintenance and repair. The bonnet is securely fastened to the body with bolts, ensuring a tight seal and preventing leakage.

Pressure Seal Bonnet Lift Check Valve:
Pressure seal bonnet lift check valves are designed for high-pressure applications. The bonnet is integral to the body and is sealed by pressure from the fluid, providing a secure seal at elevated pressures. These valves are commonly used in power generation, oil and gas, and petrochemical industries.

Welded Bonnet Lift Check Valve:
Welded bonnet lift check valves have a welded bonnet construction, where the bonnet is permanently welded to the body. This design provides enhanced strength and integrity, making it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.

Piston Lift Check Valve:
In piston lift check valves, the closing element is a piston rather than a disc. The piston moves vertically within the valve body to open or close the flow path. Piston lift check valves offer improved sealing and reduced pressure drop compared to disc-type valves, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
Spring-Assisted Lift Check Valve:
Spring-assisted lift check valves feature a spring mechanism that helps to lift the check valve disc when the forward flow pressure is insufficient to overcome gravity. This ensures positive sealing and prevents chatter or fluttering of the disc, particularly in low-pressure or low-flow conditions.
In-line Lift Check Valve:
In-line lift check valves are designed for installation directly into a pipeline without the need for additional flanges or fittings. They are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for space-constrained installations or as an economical solution.

Dual Disc Lift Check Valve:
Dual disc lift check valves feature two discs that move vertically within the valve body to open or close the flow path. This design provides improved stability and reduced pressure drop compared to single-disc valves, making it suitable for high-flow applications.
Chapter 3 - Forged Steel Lift Check Valve Application

Forged steel lift check valves find application in various industries and systems where backflow prevention is essential. Here are some common applications:
Oil and Gas Industry:
These valves are widely used in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations within the oil and gas industry. They are installed in pipelines, wellheads, manifold systems, and production facilities to prevent backflow and protect equipment such as pumps, compressors, and separators.
Petrochemical Plants:
Swing check valves are employed in petrochemical plants for controlling the flow of process fluids, including chemicals, solvents, and hydrocarbons. They are used in reactors, distillation columns, fractionation units, and storage tanks to prevent reverse flow and maintain process integrity.
Water and Wastewater Treatment:
Swing check valves play a crucial role in water and wastewater treatment plants for preventing backflow and protecting equipment such as pumps, filters, and disinfection systems. They are installed in pipelines, lift stations, and treatment facilities to maintain the flow of water and sewage in the intended direction.
Power Generation:
Swing check valves are used in power plants for controlling the flow of steam, condensate, and cooling water. They are installed in boiler feedwater systems, steam turbines, condensers, and cooling towers to prevent backflow and maintain system efficiency.
Marine and Shipbuilding:
Swing check valves are employed in marine and shipbuilding applications for controlling the flow of seawater, ballast water, and fuel oil. They are installed in piping systems aboard ships, offshore platforms, and marine vessels to prevent backflow and maintain system reliability.
HVAC Systems:
Swing check valves are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for controlling the flow of hot water, chilled water, and refrigerants. They are installed in piping networks, heat exchangers, and air handling units to prevent reverse flow and maintain thermal comfort.
Fire Protection Systems:
Swing check valves are incorporated into fire protection systems such as fire sprinkler systems and fire hydrants to prevent backflow of water or fire suppression agents. They ensure that water or foam is delivered to the fire source without interruption.
Municipal Water Supply and Distribution:
Swing check valves are used in municipal water supply and distribution systems for preventing backflow and protecting the public water supply from contamination. They are installed in water mains, pumping stations, and reservoirs to maintain the flow of potable water in the intended direction.
Chemical Processing:
Swing check valves find application in chemical processing plants for controlling the flow of corrosive chemicals, acids, and caustic solutions. They are used in pipelines, reactors, and storage tanks to prevent backflow and protect equipment from damage.









