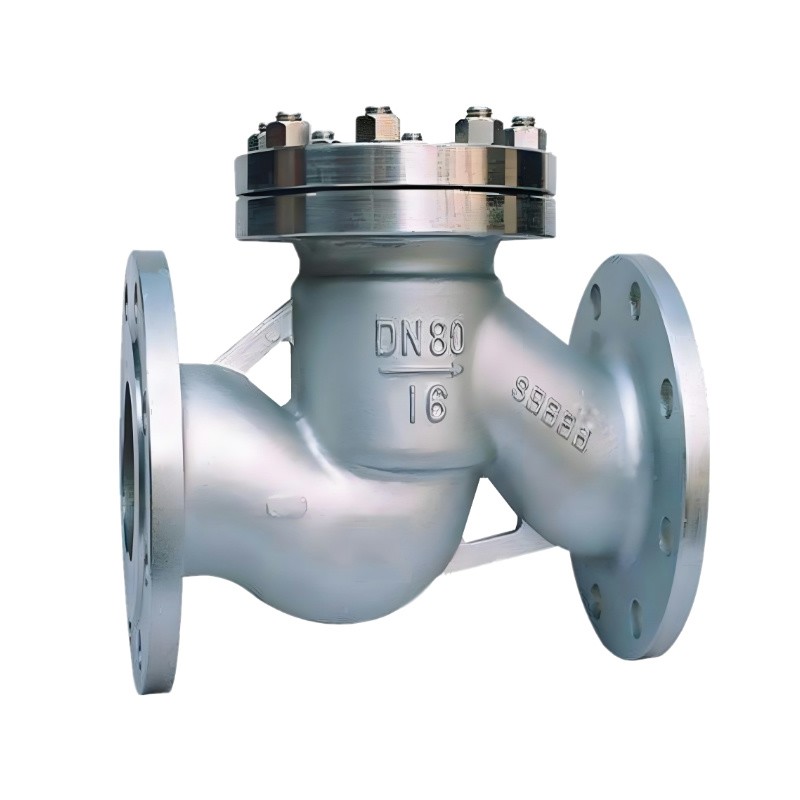
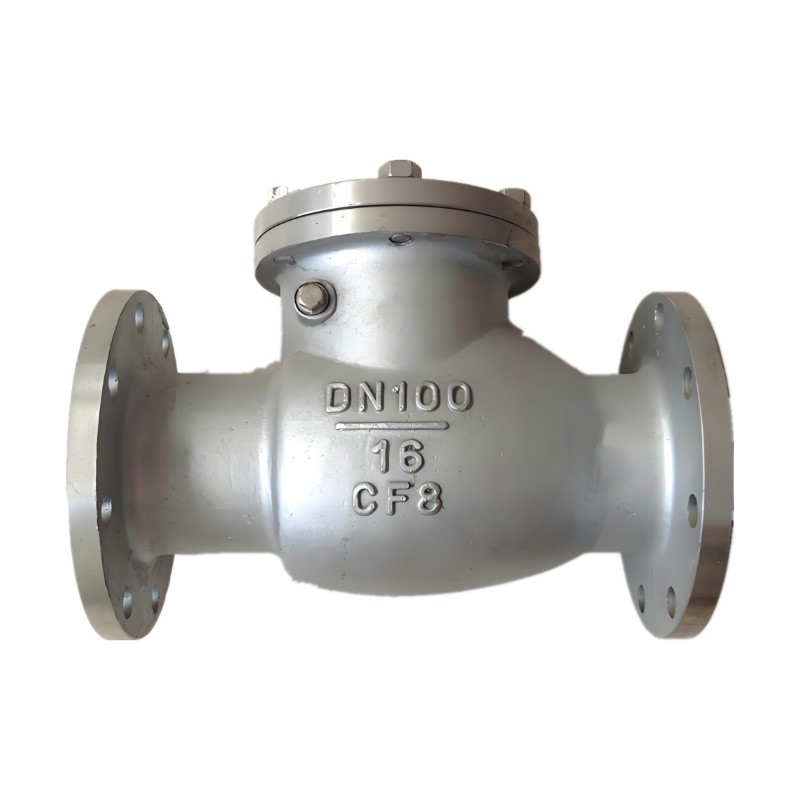
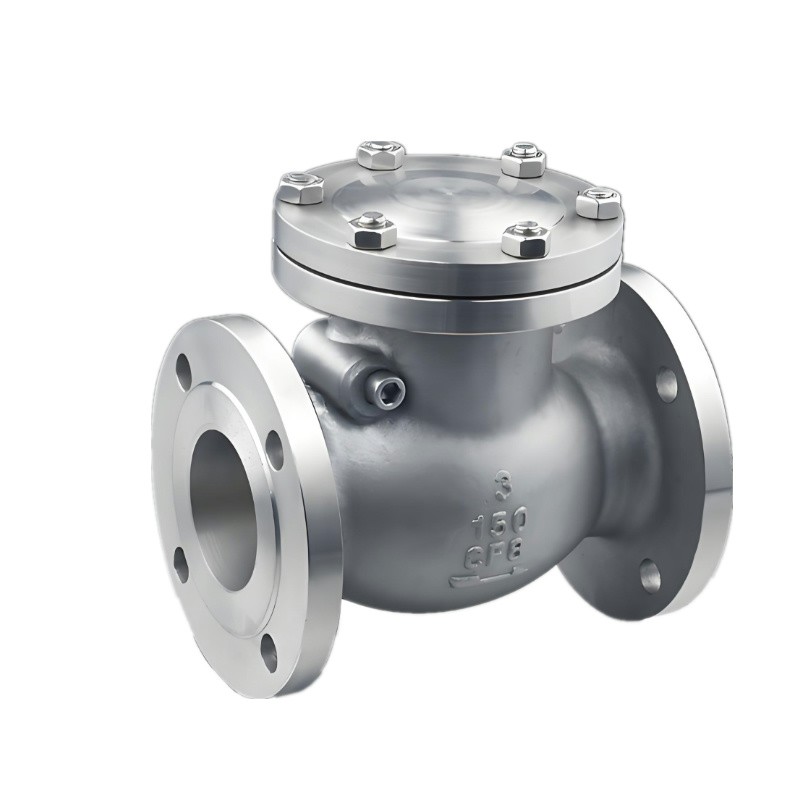
Low Temperature Check Valve
Introduction
This article contains all the information you need to know about Low Temperature Check Valve
Read further and learn more about:
Specification
Types
Application
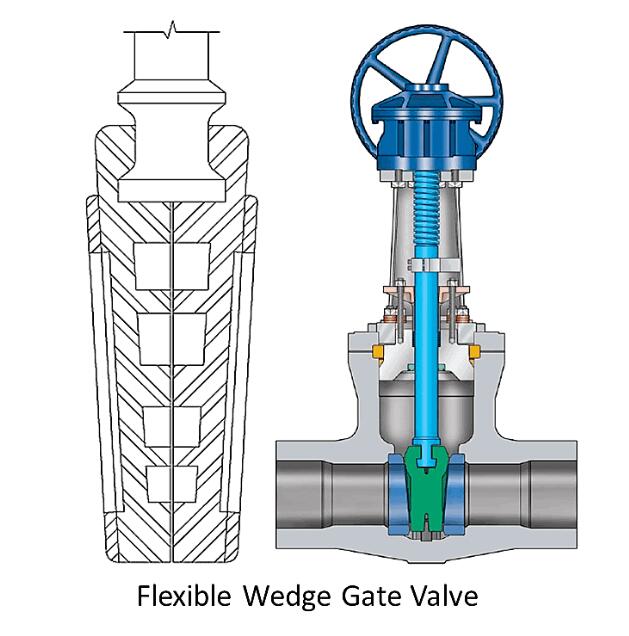
Chapter 1 - Specification
Here's a typical specification for a low-temperature check valve:
Body Material
For low-temperature applications, the valve body material is typically selected from materials suitable for cryogenic service, such as stainless steel (ASTM A351 CF8M or CF8), carbon steel (ASTM A216 WCB), or alloy steel (ASTM A217 WC6 or WC9).
Trim Material:
Trim materials should be selected for compatibility with low temperatures and the fluid being handled. Trim materials may include stainless steel, alloy steel, or other suitable materials with cryogenic properties.
Seat Material:
The sealing material should be selected based on compatibility with low temperatures and the fluid being handled. Common sealing materials for low-temperature applications include PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), graphite, or metal-to-metal seals.
Valve Size
Available in various sizes typically ranging from 1/2" to 24" (larger sizes may be available upon request).
Bonnet Type:
Bolted bonnet design or pressure seal bonnet design, depending on the pressure rating and application requirements.
Pressure Rating
ANSI Class 150, 300, 600, or higher, indicating the maximum pressure the valve can withstand. The selection of pressure rating depends on the specific application requirements.
Temperature Range
Suitable for low-temperature applications ranging from -196°C to -29°C (-321°F to -20°F) or even lower, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
End Connections
Flanged, butt weld, or socket weld ends, conforming to relevant ASME standards such as ASME B16.5, ASME B16.25, or ASME B16.11, respectively.
Design Standards:
The valve design should comply with industry standards such as API 594, API 6D, or ASME B16.34 for construction, design, and testing requirements specific to check valves.
Compliance:
The valve should comply with relevant industry standards and regulations such as ASME, ANSI, API, ASTM, MSS-SP, and others, depending on the application and location.
Chapter 2 - Low Temperature Check Valve Types
While swing check valves generally follow a similar operational principle, they can vary in design and configuration to suit different applications and requirements. Here are some common types of swing check valves based on their design:

Basic Swing Check Valve:
This is the standard design of a swing check valve, featuring a hinged disc that swings open in response to forward flow and closes under reverse flow to prevent backflow. It is the simplest and most commonly used type.

Tilting Disc Check Valve:
In this design, the disc is mounted on a hinge pin and can tilt slightly to allow for smoother operation and reduce wear on the sealing surface. Tilting disc check valves are suitable for applications with high flow rates or frequent cycling.

Dual Plate Check Valve:
This type of check valve features two semicircular discs that are hinged in the center and swing open or closed in response to flow direction. Dual plate check valves offer reduced pressure drop and faster response times compared to traditional swing check valves.

Wafer Check Valve:
Wafer check valves are designed to fit between two flanges and are held in place by the flange bolts. They are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for space-constrained installations. The swing disc design is similar to basic swing check valves.

Lift Check Valve:
Lift check valves feature a disc that moves vertically (upward or downward) to allow or prevent flow. They are commonly used in applications where space is limited or where rapid closing is required to prevent water hammer.
In-line Check Valve:
In-line check valves are designed to be installed directly in a pipeline and do not require additional flanges or fittings. They are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for use in tight spaces or as an economical solution.
Silent Check Valve:
Silent check valves are designed to minimize noise and water hammer by incorporating features such as spring-loaded discs or dashpots to control the closing speed of the valve. They are commonly used in residential and commercial plumbing systems.
API 6D Swing Check Valve:
These swing check valves are designed and manufactured according to API 6D standards, which specify requirements for design, materials, testing, and inspection. They are commonly used in oil and gas production, refining, and pipeline applications.
Chapter 3 - Low Temperature Check Valve Application

Low-temperature check valves find application in various industries and systems where the handling of cryogenic fluids or gases is involved. Here are some common applications:
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Industry:
Low-temperature check valves are extensively used in LNG processing facilities, storage tanks, and transportation systems. They ensure the safe and reliable flow of liquefied natural gas at extremely low temperatures, typically below -162°C (-260°F), to prevent backflow and maintain system integrity.
Industrial Gas Storage and Distribution:
These valves are employed in facilities that handle industrial gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and hydrogen. They are installed in cryogenic storage tanks, pipelines, and distribution systems to prevent backflow and ensure the safe and efficient handling of cryogenic gases.
Air Separation Plants:
Low-temperature check valves play a crucial role in air separation plants where atmospheric air is liquefied and separated into its components (nitrogen, oxygen, and argon) through cryogenic distillation. They are used in various process streams to prevent backflow and maintain separation efficiency.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Terminals:
Low-temperature check valves are utilized in LPG terminals and distribution systems for handling liquefied petroleum gases such as propane and butane. They help to maintain the flow of LPG at low temperatures and prevent the risk of leakage or spillage.
Cryogenic Storage and Transportation:
These valves are installed in cryogenic storage vessels, tankers, and transport pipelines used for storing and transporting cryogenic liquids such as liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, and liquid hydrogen. They ensure the integrity of the storage and transportation systems by preventing backflow and leakage.
Medical and Healthcare:
These valves are utilized in medical and healthcare facilities for handling cryogenic liquids used in medical imaging (MRI), cryosurgery, cryopreservation, and other medical applications. They help to maintain the integrity of cryogenic equipment and ensure patient safety.
Food and Beverage Industry:
Low-temperature check valves may also find application in the food and beverage industry for handling cryogenic fluids used in food freezing, chilling, and preservation processes. They help to maintain food quality and safety by preventing contamination and ensuring proper handling of cryogenic fluids.








